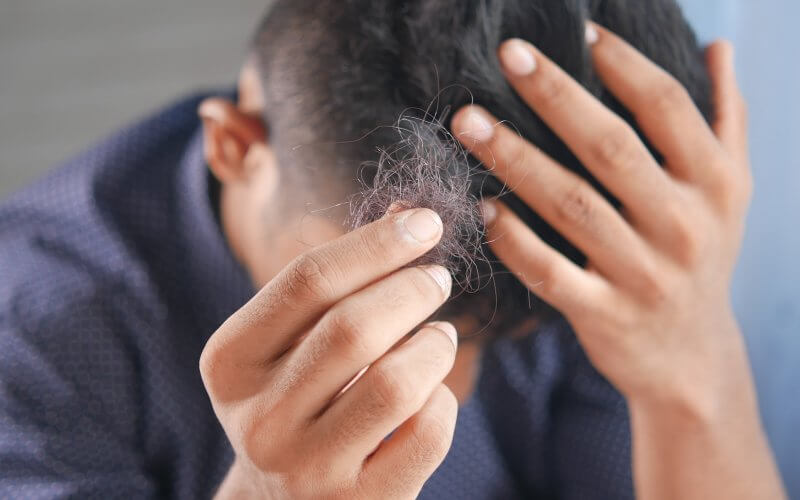
Hair loss can be a distressing experience for both men and women, impacting self-esteem and overall well-being. While there are various factors that contribute to hair loss, including genetics, hormonal changes, and lifestyle choices, certain medications can also play a significant role. In this article, we will explore five commonly prescribed medications that have been associated with hair loss and discuss the importance of understanding the potential side effects of these drugs.
1. Chemotherapy Drugs
Chemotherapy is a well-known treatment for cancer, targeting rapidly dividing cells in the body. Unfortunately, while it effectively combats cancer cells, it can also affect healthy cells, including those responsible for hair growth. Hair loss is a common side effect of chemotherapy, and it can occur all over the body, including the scalp, eyebrows, and even eyelashes. The extent and duration of hair loss depend on the specific chemotherapy drugs used and the individual’s response to treatment.
Although hair loss during chemotherapy is often temporary, it can still be emotionally challenging. Many individuals opt to wear wigs, scarves, or hats during this period to maintain their confidence and sense of self. It’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals and support networks to explore coping strategies and potential hair regrowth options post-treatment.
2. Anticoagulants
Anticoagulants such as Heparin and Warfarin, commonly known as blood thinners, are prescribed to prevent blood clotting and reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes. While these medications are crucial for many patients, they can sometimes cause hair loss as a side effect. Warfarin and heparin are two anticoagulants that have been associated with hair loss in some individuals.
Hair loss related to anticoagulant use may be reversible once the medication is discontinued. If you are experiencing hair loss while taking anticoagulants, it is important to consult your healthcare provider. They can assess your situation and recommend alternative treatment options if necessary.
3. Antidepressants
Antidepressant medications such as Paxil and Zoloft and Lexapro are commonly prescribed to manage various mental health conditions, including depression and anxiety. While these medications provide much-needed relief for many individuals, they can also have side effects, including hair loss. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), a class of antidepressants, have been linked to hair loss in some cases.
Hair loss caused by antidepressants is usually temporary and will often reverse once the medication is adjusted or discontinued. It is crucial to discuss any concerns about hair loss with your prescribing physician. They can assess your situation and make appropriate changes to your treatment plan, ensuring both your mental health and physical well-being are taken into consideration.
4. Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers such as Metoprolol and Atenolol are medications commonly prescribed for conditions such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and migraines. While they effectively manage these conditions, they can sometimes cause hair loss as a side effect. Examples of beta-blockers include propranolol, atenolol, and metoprolol.
Hair loss related to beta-blocker use may be temporary, and hair growth can resume once the medication is adjusted or discontinued. It is important to communicate with your healthcare provider if you are experiencing hair loss while taking beta-blockers. They can evaluate your situation and recommend alternative medications or adjust the dosage as needed.
5. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and manage fever. Medications such as ibuprofen, naproxen, and celecoxib (Celebrex) fall into this category. While hair loss is not a common side effect of NSAIDs, some individuals have reported experiencing it while taking these medications.
If you notice hair loss while taking NSAIDs, it is essential to consult your healthcare provider. They can determine if there is a correlation between the medication and your hair loss and suggest alternative pain management strategies or adjust the dosage if necessary.
It’s important to note that not everyone who takes these medications will experience hair loss. The occurrence of this side effect can vary from person to person, depending on factors such as individual sensitivity, dosage, and duration of medication use. If you have concerns about hair loss while taking any medication, it is always advisable to seek medical advice.
In addition to these medications, it is worth mentioning that certain other drugs, such as acne medications such as isotretinoin (Accutane) and tretinoin (Retin-A), immunosuppressants including methotrexate, leflunomide (Arava), cyclophosphamide, and etanercept (Enbrel), and some cholesterol-lowering drugs such as simvastatin (Zocor) and (atorvastatin) Lipitor, have also been associated with hair loss in some cases. It is crucial to read the medication package inserts and consult with your healthcare provider to understand the potential side effects before starting any new treatment.
If you are experiencing hair loss due to medication use, here are some additional steps you can take to manage the situation:
- Consult your healthcare provider: Discuss your concerns about hair loss with your prescribing physician. They can evaluate your situation, provide guidance, and recommend appropriate alternatives or adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Explore hair regrowth options: Depending on the cause and extent of hair loss, there may be various options available to stimulate hair regrowth. These can include topical treatments, dietary supplements, or other medical interventions. Your healthcare provider can provide recommendations based on your specific circumstances.
- Consider support networks: Hair loss can be emotionally challenging, and it can be helpful to connect with others who have gone through similar experiences. Support groups or online communities can provide valuable advice, encouragement, and empathy during this time.
- Adopt healthy hair care practices: While medication-induced hair loss may be temporary, taking care of your hair and scalp can promote overall hair health. Use gentle hair care products, avoid excessive heat styling or harsh treatments, and maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals that support hair growth.
- Utilize prescription discount programs: Medications can be costly, and managing hair loss due to medication use may involve additional expenses. Utilizing prescription discount programs like RxGo can help reduce the financial burden by providing access to discounted medication prices. These programs can be valuable resources in managing overall healthcare costs.
In conclusion, it’s important to be aware that hair loss can be a potential side effect of certain medications. Understanding these risks and discussing them with your healthcare provider before starting any new treatment can help you make informed decisions about your health. If you experience hair loss while taking medication, consult your healthcare provider for guidance and explore available options to manage and potentially reverse the effects. Remember, you are not alone, and support is available to help you navigate this challenging experience.
Note: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be substituted for professional medical advice. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and treatment options.